New global alliance launched to end AIDS in children by 2030
MONTREAL/GENEVA/NEW YORK, 1 August 2022 - UNAIDS
MONTREAL/GENEVA/NEW YORK, 1 August 2022 - UNAIDS
Mettre fin au sida chez les enfants, grâce à une alliance forte, stratégique et orientée vers l’action de parties prenantes multisectorielles aux niveaux national, régional et mondial qui travaille avec des femmes, des enfants et des adolescents vivant avec le VIH, des gouvernements nationaux et des partenaires pour mobiliser le leadership, le financement et l’action afin d’en finir avec le sida chez les enfants d’ici 2030.
An end to AIDS in children, achieved through a strong, strategic, and action-oriented alliance of multisectoral stakeholders at national, regional, and global levels that works with women children and adolescents living with HIV, national governments, and partners to mobilize leadership, funding, and action to end AIDS in children by 2030.
An end to AIDS in children, achieved through a strong, strategic, and action-oriented alliance of multisectoral stakeholders at national, regional, and global levels that works with women children and adolescents living with HIV, national governments, and partners to mobilize leadership, funding, and action to end AIDS in children by 2030.
MONTREAL, 30 July 2022 — UNAIDS
The AIDS 2022 Roadmap outlines conference and pre-conference sessions related to children, adolescents and pregnant women, taking place at the 24th International AIDS Conference virtually and in Montreal, Canada from 29 July to 2 August, 2022. Access the full programme here.
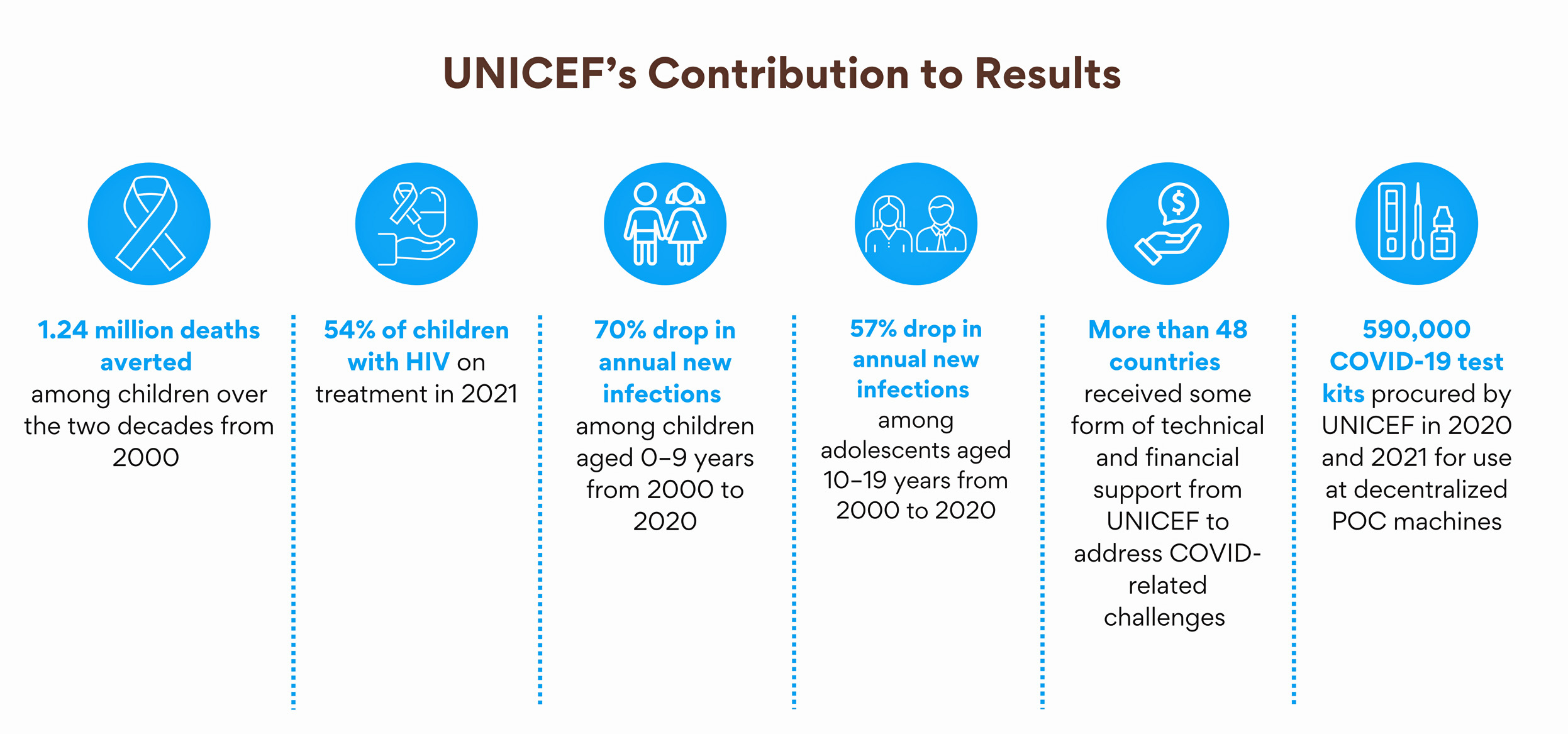
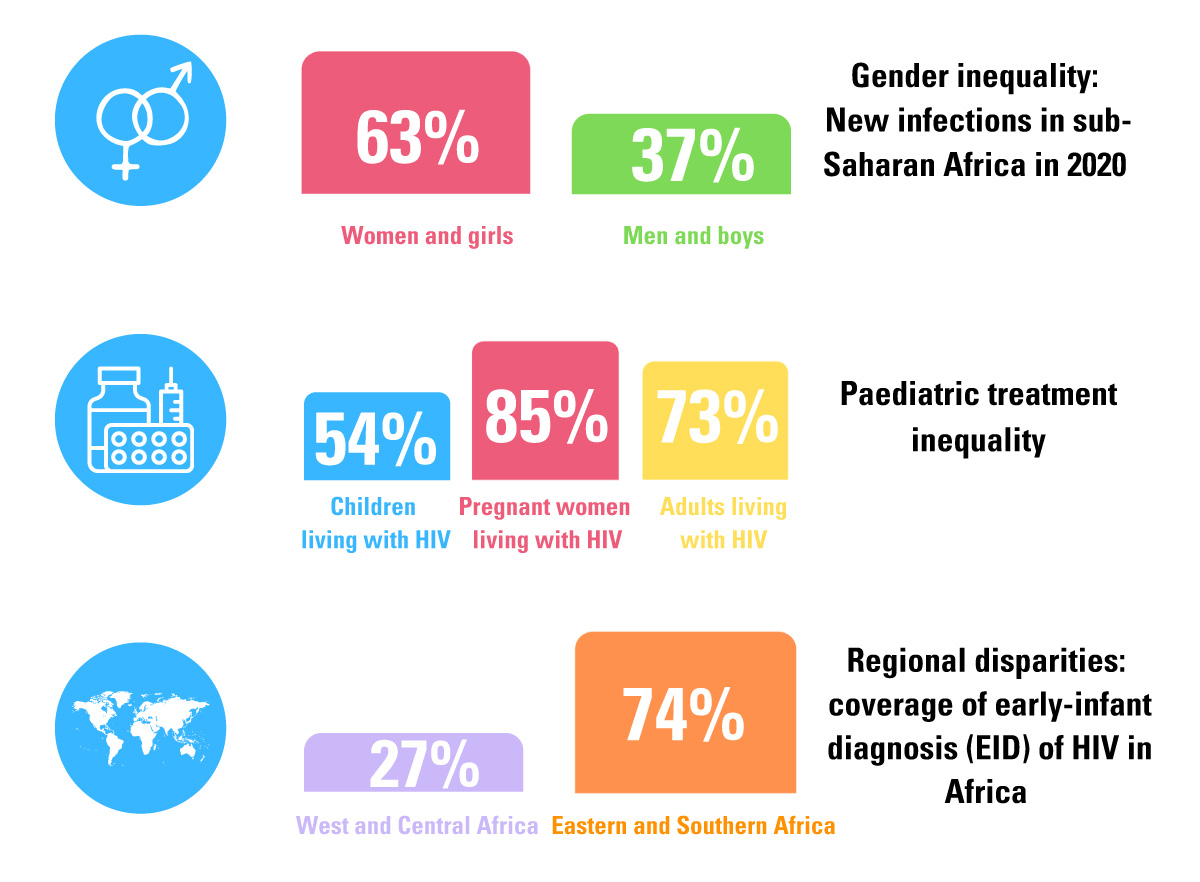
It is clear that the AIDS epidemic is not over. The pace of progress is too slow to meet the 2030 SDG targets. To promote faster and more consistent improvement, the new UNICEF Strategic Plan emphasizes differentiation, integration, partnership and innovation to address barriers to inequalities.
This brief addresses integration of HTS into FP services. It is intended as a practical resource for national health programmes seeking to introduce or scale up HIV testing and linkage to HIV prevention, STI, and antiretroviral therapy (ART) services in FP.
This report presents the results of a mapping of HIV-sensitive social protection programmes in 15 'fast track' countries in eastern and southern Africa. The exercise, commissioned by WFP and ILO, aimed at understanding how existing social assistance and social security programmes in the region are integrating the vulnerabilities exacerbated by HIV.
Social protection can be a critical enabler of efforts to reduce HIV risks, mitigate their impacts, and increase the capacity of households to cope and respond to the risks. Social protection can also be used as an entry point to address deeply rooted social vulnerabilities and structural factors faced by those who are vulnerable to HIV infection.
This document provides a compilation of tools, best practices and guidelines that facilitate the integration of interventions and services to address the interlinked issues of mental health and HIV. It emphasizes the importance of integrating HIV prevention, testing, treatment and care; mental health services and care for people living with HIV.