ALL In to #EndAdolescentAIDS
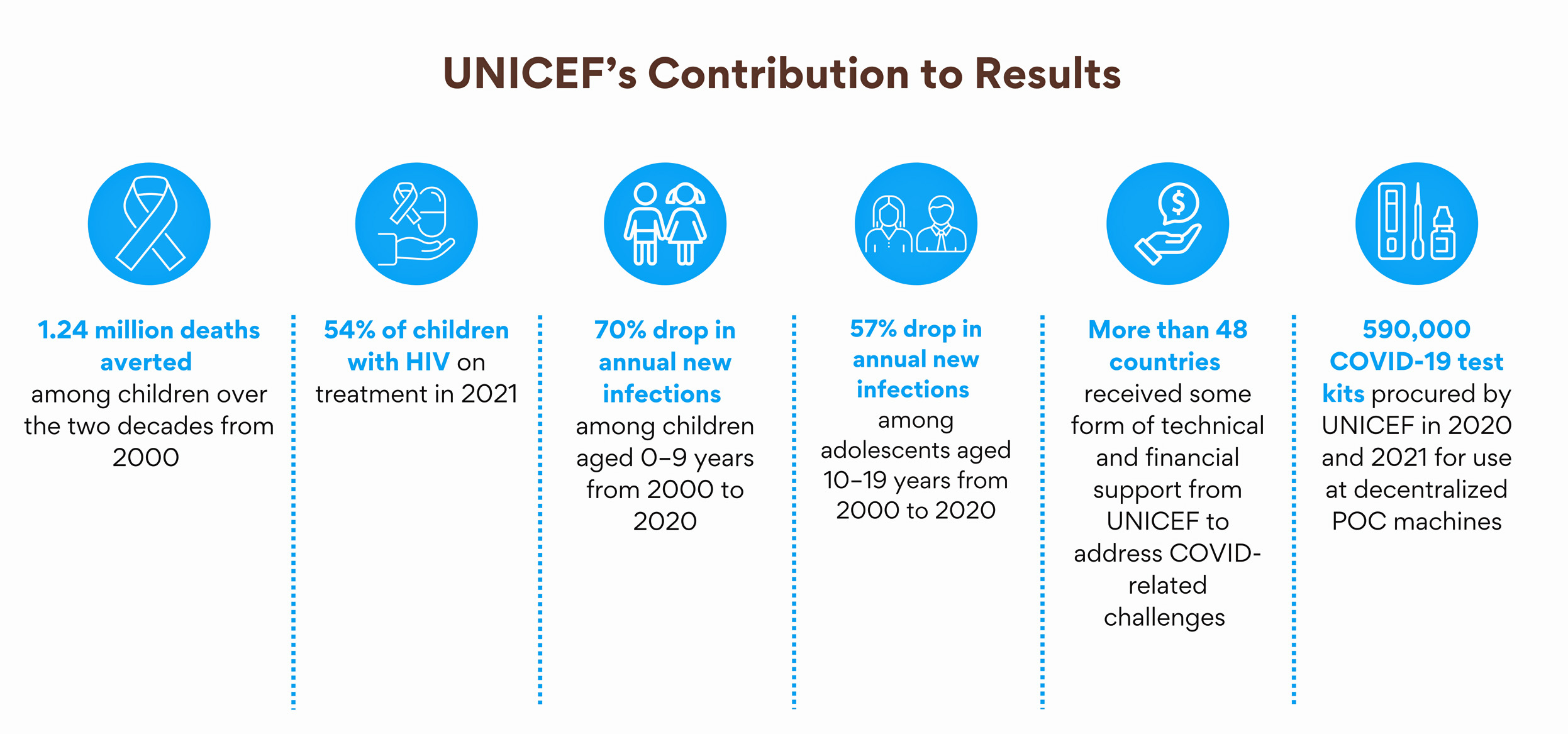
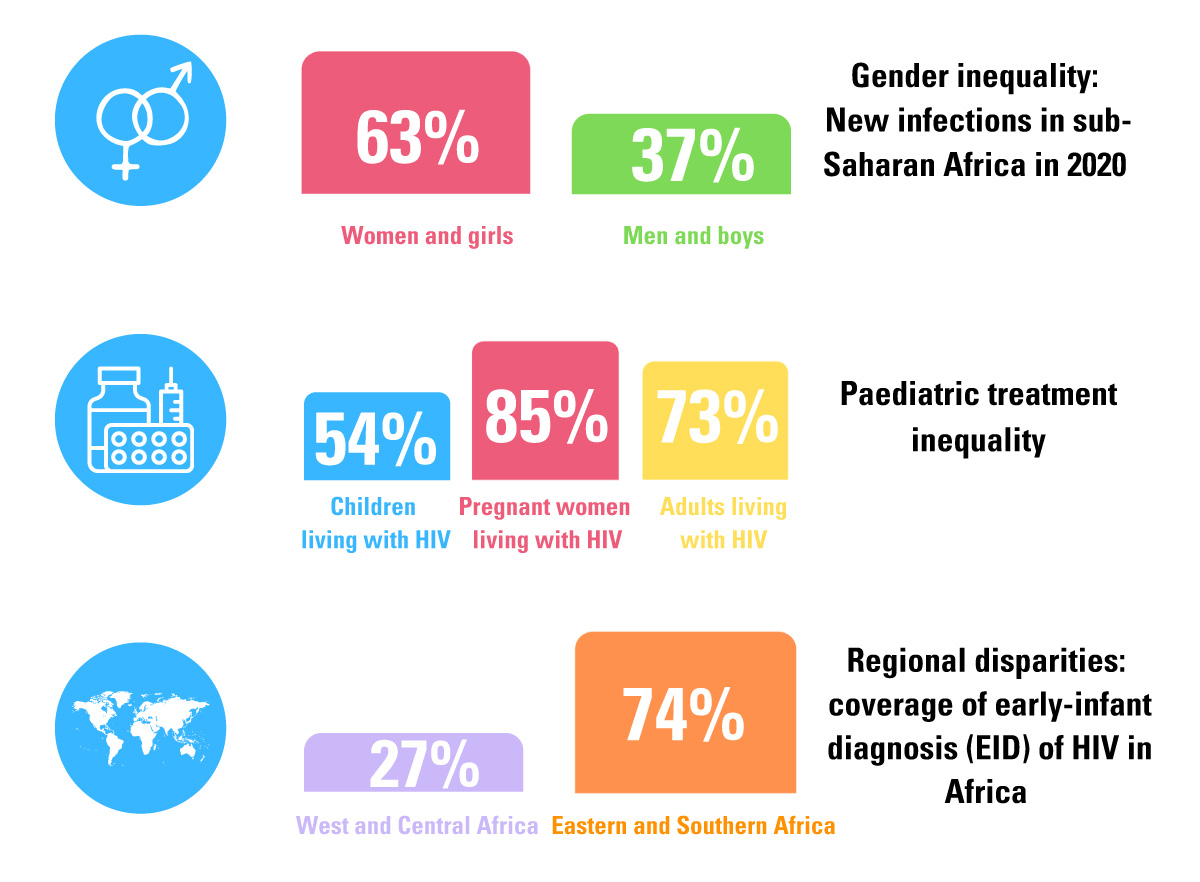
Around the world, an estimated 2.1 million adolescents between the ages of 10 and 19 years were living with HIV in 2016. Some 260,000 older adolescents (aged 15–19 years) were newly infected with HIV in 2016, or nearly a new infection every two minutes. Nearly three out of four new infections occurred in sub-Saharan Africa. And adolescent girls continue to be disproportionately affected. Globally, nearly two thirds (65 per cent) of new HIV infections among adolescents aged 15–19 years were among girls.
Progress in preventing new infections among adolescents remains unacceptably slow, with new infections declining by only 14 per cent since 2010. Equally concerning, between 2000 and 2015, annual AIDS-related deaths declined for all age groups except adolescents (aged 10–19 years).
Demographic realities further undermine recent hopeful trends. In sub-Saharan Africa, the region most affected by HIV, the youth population has begun to explode in size and will continue to do so, with projections indicating that the number of people younger than 20 will double in 2030. That means redoubled efforts will be necessary to prevent an increase in new HIV infections among adolescents.
The ALL IN agenda was introduced to drive social change for better results in adolescents, to improve strategic prioritization and programming for adolescents, and to foster innovation and advocacy to ensure that countries build stronger, more sustainable systems; engage adolescents in the response and provide quality health care. It is a Fast-Track response for adolescents—linked to the Three Frees initiative ('Start Free', 'Stay Free', 'AIDS Free') to accelerate service delivery towards attaining both the 90–90–90 and adolescent specific targets.